Introduction
This is a blog we've been meaning to write for a long time, but for reasons that will soon become apparent, we had to wait until we'd completed our factor investing research before writing it.
I have previously mentioned how I was continually approached by financial advisers attempting to sell me outperforming funds when I worked in the city. At the time, I couldn't work out how they were giving the illusion of outperformance, but I knew that it was unlikely to be genuine, given the competitiveness of the markets.
This blog details what I subsequently learnt and should give you the information necessary to ask the right questions if someone tries to sell you some magic (beans)!
What is a star fund manager?
Much like stellar evolution, we believe star fund managers follow a well-defined trajectory:
Nebula: The star fund manager demonstrates (supposed) outperformance versus a benchmark.
Dwarf: The press picks up on this and positions the fund manager as Britain's answer to Warren Buffett. The fund appears on the investment platforms' "best buy" lists, and investors start to notice.
The question is, is there any genuine magic? And what are the subsequent stages in a star fund manager's lifecycle?
How do we analyse performance? CAPM?
I mentioned previously that we wanted to finish our factor research before addressing star fund managers. This research examined the CAPM model and how it predicted returns based on risk relative to the market.
We have created a series of imaginary stock market returns, as shown below.
We have also created a series of returns for a fund manager whose fund we shall call "Buying quality companies at good prices", or BQCAGP for short.
Based on the above, BQCAGP appears to have beaten the market, growing £100,000 into £226,105 after ten years versus the overall market, with a finishing balance of £216,202.
Legendary crooner Barry Manilow once pondered, "Could it be Magic?" - we should ask ourselves the same question.
Fama-French - peeling back the magician's curtain
In our factor research post, we discussed the Fama-French three-factor model, which attempted to address some shortcomings of the CAPM approach and more accurately reflect the drivers of investment returns.
We will now add the returns of the factors over the decade to our existing market returns and analyse how this has impacted BQCAGP from exposures taken towards (or against) the value (growth) and small (large) factors.
BQCAGP has factor tilts towards large-cap and growth and sits in the top right corner of the style box.
If we now analyse BQCAGP's performance by considering the fund's factor tilts rather than just using the single factor CAPM, we can now see that the "outperformance" can be explained by these factor tilts.
Market balance after ten years: £216,202
Growth factor return: (£164,514-£100,000)*10% = £6,451
Large factor return: (£134,516-£100,000)*10% = £3,452
Total = £226,105
The above is a (massively!) simplified example. For those who want to dig deeper, there is some excellent research by investment management firm AQR Capital Management. They analyse the returns of two well-known U.K. fund managers, Terry Smith and Neil Woodford (during the Invesco years). In both cases, they determined no statistically significant alpha (alpha measures outperformance (or underperformance) versus the market). For those who have read our previous blog posts, this should come as no surprise. The financial markets are brutally competitive, and some firms have resources that dwarf those available to retail fund managers. AQR also undertook a similar analysis on legendary investor Warren Buffett and also found no evidence of statistically significant alpha.
So why should this matter to you as a private investor? Below, we identify the potential problems that an investor should consider.
Problem 1: You are potentially accepting more risk
Our examples above demonstrated that taking tilts away from the value and small factors (towards growth and large companies) enabled BQCAGP to "outperform" the overall market - this has also been the case for live markets over the last decade.
If we look at the value factor, we can see that it has far underperformed the overall market (143% vs 224%) and growth (315%).
However, during 2022, growth underperformed the market by over 10%, and many managers who had tilted towards growth shares also suffered.
During the decade from 2000 to 2010, we also saw growth that underperformed the overall market.
We've written before about why we think holding a portfolio containing 100% equities might not be the optimal approach for many retirees. We'd suggest that a portfolio containing 100% equity with factor tilts to growth may be even worse! Many may be unprepared for the large drawdowns - from the start of 2000 to the end of 2002, the growth index fell by over 50%! This may be devasting to the income sustainability of a retirement portfolio.
Of course, you could aim to time your exposure to fund managers, taking advantage of their different factor styles, but much like timing the markets, this is challenging to do in reality!
Problem 2: Performance chasing
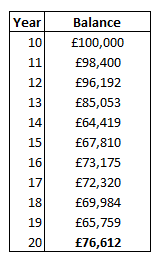
We recently covered the downside of performance chasing and how it can blow up your retirement plan. Let's now return to our BQCAGP fund. After several years of "outperformance," investor money has flooded into the BQCAGP fund, which has become a red supergiant.
Alas, the subsequent decade is not so kind (see 2000-2010 above for how bad things can get!) to the BQCAGP fund and investors, both from an overall market perspective and the fund's large and growth tilts, which have been a drag on returns.
From a starting balance of £100,000 at the start of year 11, the balance of BQCAGP has shrunk to £76,612, compared to £97,424 for the overall market.
Investors who piled into the fund (typically towards years 8-10 when the great returns were almost over!) now find themselves trailing the market by a large amount and start to withdraw their money. The fund dramatically shrinks in size and becomes a white dwarf (star experts might see a problem here!). The fund house considers closing the fund to avoid having to show potential clients examples of their underperforming funds. This is survivorship bias in action and something potential investors should be aware of.
Problem 3: Manager style drift risk
"Buying undervalued companies hoping they recover" (BUCHTR) is another of our example funds. They have a small-cap value tilt, and as might be expected, the first decade is painful.
They return £208,618 versus the overall market with a balance of £216,202.
Fed up with not attracting investor inflows after the first decade, BUCHTR decided to take heavy factor tilts towards large growth factors (more than BQCAGP), only to suffer for a second decade!
BUCHTR's investors have suffered for two decades, but at least the funds are liquid, and investors can withdraw their money at any time. This may not always be the case, and the fund may well develop into the dreaded black hole, with investors struggling to get their money back.
Problem 4: Fees
Given the above analysis from AQR showing that genuine outperformance is rare even among superstar fund managers, investors should ask themselves whether it is worth paying these fees when you can buy a low-cost, globally diversified portfolio for a fraction of the cost. We often save new clients money when they engage with us as they previously paid high fund manager fees.
Problem 5: Concentration Risk
We believe diversification is key to generating sustainable portfolio income, and our portfolios typically contain over 10,000 holdings (a mix of shares and bonds).
In contrast, some fund managers hold less than 30 shares. This is understandable, as they are often attempting to outperform the market. The more shares they hold, the more the fund behaves like the overall market (therefore reducing the chance of outperformance). If one or more shares in the concentrated portfolio run into difficulties, this can significantly impact the performance of the overall fund.
Another aspect to consider is sector concentration. The diagram below shows two imaginary funds, one an index tracker and one run by an active fund manager. The index “buys the world” with equal amounts in the ten underlying sectors. By contrast, the active fund manager is more selective because their chosen investing stance might be better served by a particular sector. For example, they might have a large-cap growth style we have explored above, and this type of share might predominate in the consumer defensive sector. Consider the implications for the active portfolio were the consumer defensive sector takes a hit.
Of course, an investor could add more than one actively managed fund to the portfolio, but there may be challenges around overlapping holdings, and maintaining this portfolio can become more complicated, especially given the decline in financial literacy as we age.
Problem 6: Lack of historical data
We have the good fortune of having over a century of historical market data on which to base our retirement planning, and we sometimes wonder whether this is sufficient (see challenge three in our 4% rule analysis). In contrast, fund managers typically run a given fund for a decade or less. Given these timeframes, we'd find it very difficult to build a robust retirement income strategy, particularly with the ever-present risk of style drift (see problem three).
Conclusion
If we're honest, we can see the (superficial) appeal of investing with star fund managers. You are being given access to some of the investment magic at what seems a reasonable fee. However, given the overwhelming evidence, we'd struggle to consider it a better option than the relatively boring, low-cost, globally diversified portfolio, which is how we invest our clients' money.
A summary of the risks of the three investing options is shown below.
Want to find out more?
Please contact us if you want to build a retirement plan that gives you the best chance of retirement success.
About us
The team at Pyrford Financial Planning are highly qualified Independent Financial Advisers based in Weybridge, Surrey. We specialise in retirement planning and provide financial advice on pensions, investments, and inheritance tax.
Our office telephone number is 01932 645150.
Our office address is No 5, The Heights, Weybridge KT13 0NY.
Please note: This blog is for general information only and does not constitute advice. The information is aimed at retail clients only.
Although best efforts are made to ensure all information is accurate, you should not rely on this blog for your personal situation or planning.
The value of your investment can go down as well as up and you may not get back the full amount you invested. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance.



















Comments